How Many Pints Of Blood Are In The Human Body?
The number of pints of blood in the human body is 10.5 pints. There are about 10.5 pints of blood in the average adult human body, but this can age and extent. It accounts for nearly 7–8% of body weight. A single pint of actuality can drop without causing any harm to the body.
How Many Pints of Blood are in the Human Body?
The amount of blood in the human form of course, dependent on the human. A person’s age, sex, body size, and general health affect their blood pressure. Usually, though, the mature human body contains around 10.5 pints of blood. Put another way, that’s about 5 liters, or 1.3 million.
To put those statistics into perspective, that’s about 8-10% of a stable adult’s body weight. A regular-sized human has about 8-10 pints of blood, in which is nearby 8% of the body’s weight. Half of the blood is equivalent to 473.18 milliliters.
Men vs Women
Men typically have more blood than women due to their usually greater body size and muscle frame. Notably, pregnant women are outliers, with a roughly 50% development in blood pressure.
New Children
The regular newborn has about a sector of a liter of blood, which amounts to about half a pint.
Newborn (6-12)
Like children, children in this age group have about 70 mLs of plasma per kg. That income is enough for a 66-pound child to have around 2 liters of blood mingling in their body.
An Evaluation Table (Men vs Women vs Children)
| Group | Regular Blood Pressure | Average Blood Pressure (L) | Key Notes |
| Men | 9–10 | 5–6 L | High blood pressure due to greater body size and increased mass. |
| Women | 8–9 | 4.5–5 L | Slightly lower pressure than men; differs with body size and pregnancy. |
| Children | 4–6 | 2–3.5 L | Blood pressure surges with age, height, and weight. |
| Babies | 1–2 | 0.5–1 L | Blood pressure is small but proportionately high relative to body weight. |
Factors That Affect Blood Pressure
| Factor | How It Affects Blood Pressure |
| Body Size & Weight | Bigger and heavier individuals usually have higher total blood pressure. |
| Gender | Grown men typically have more blood than women due to a larger muscle frame and greater frame mass. |
| Age | Children have lower blood pressure; as the body produces more blood, blood pressure increases. |
| Pregnancy | Blood pressure by 30–50% to support. |
| Hydration | Dryness reduction; plasma pressure; hydration helps preserve normal levels. |
| Fitness | Athletes often experience higher blood pressure and a higher red blood cell count. |
| Height | Living at an altitude increases red blood cell production to improve oxygen transport |
| Medical | Conditions such as anemia, heart disease. If kidney disease can affect blood pressure. |
| Blood Loss | Injury, surgery, or heavy flow can temporarily lower blood pressure. |
| Medicines | Drugs or solutions can reduce blood pressure on their own |
Why Blood Pressure Matters
| Aspect | Why Blood Pressure |
| Oxygen Passage | Ensures enough oxygen is carried to tissues and organs for proper function. |
| Nutrient Supply | Cells allocate essential nutrients, such as glucose, vitamins, and minerals, to themselves |
| Waste Deletion | Passages carbon dioxide and metabolic waste to lungs and kidneys for elimination. |
| Blood Pressure Control | Maintains normal blood pressure and healthy circulation. |
| Structure Function | Chains the heart, brain, kidneys. And also, A liver by ensuring adequate blood supply. |
| Safe Security | Helps white blood cells fight poisons and irritation. |
| Temperature Rule | Distributes heat throughout the body to maintain stable body temperature. |
| Hormone Transport | Carries hormones to target organs to regulate body processes. |
| Injury Reply | Enables the setting to prevent excessive blood loss during injuries. |
| Overall Being | Too little or too much blood pressure can be dangerous. |
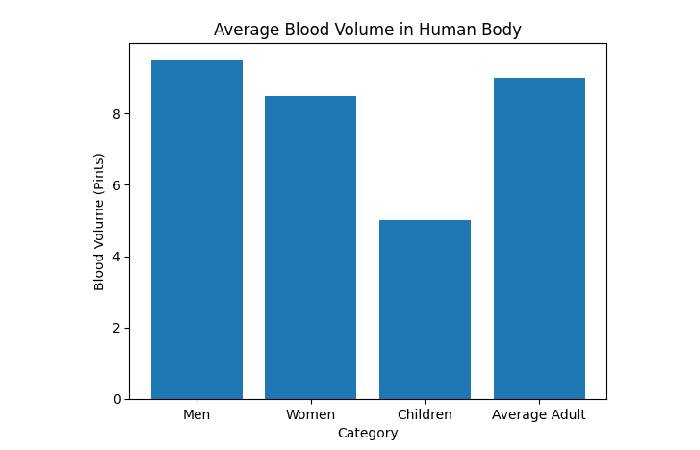
Average Blood Volume In The Human Body
Composition of Blood
| Blood Constituent | Percentage of Blood | Function |
| Plasma | 55% | The liquid portion that conveys nutrients, hormones, proteins, and waste products. |
| Red Blood Cells | 40–45% | Carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues and carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs. |
| White Blood Cells | <1% | Defend the body against poisons and foreign invaders. |
| Platelets | <1% | Help in plasma clotting to prevent extreme bleeding. |
| Plasm Proteins | Part of plasma | Include albumen, globulins, and fibrinogen; preserve osmotic pressure and protection. |
| Nutrients | Part of plasma | Support cell meaning, nerve signaling, and absorption. |
Plasma
Blood plasma is the intravascular liquid constituent of blood after blood cells are detached. Plasma holds proteins and other blood components. It makes up about 55% of the body’s total blood pressure.
Plasma is 95% water and contains essential dissolved proteins like serum albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen. And also, It glucose, coagulation factors, electrolytes Na+, Ca2+, Mg2+, HCO3-, Cl-, etc. It hormones, carbon dioxide, and oxygen. In which makes up about 6%-8%. It has an intravascular osmotic effect that maintains electrolyte balance. And also, It protects the body from toxins and other bloodborne illnesses.
Blood Cells
About 50% of blood consists of three main types of blood cells: platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells. Most blood cells are designed by a single type of unspecialized cell current inside the soft fatty tissue of the bone cavity.
Red blood cells contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to tissues and helps them function correctly.
White blood cells are part of the resistant system and belong to five different types: neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. These assistants protect against infections and have a role in irritation and allergic responses.
Platelets are small cells that play a vital role in blood clotting. And also, The closure of micro-punctures in the body.
The rate of blood cell manufacture is skillful by demand. The typical lifespan of blood cells ranges from a few periods for white blood cells. In to about 10 days for platelets and about 120 days for red blood cells.
Proteins
Plasma proteins perform numerous vital functions, including the transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins, and minerals. Some proteins act as enzymes, complement devices, peptidase inhibitors, or kinin forerunners. The three key plasma proteins contain albumen, globulin, and fibrinogen.
Serum albumin makes up about 55% of blood proteins. It maintains plasma oncotic pressure (preventing fluid accumulation and helping retain solutions. In the vascular compartment) and acts as a carrier for fat-soluble and steroid hormones.
Globulins make up about 38% of blood proteins. They help transport ions, hormones, and lipids, and are essential to the body’s resistant system.
Fibrinogen types about 7$ of blood proteins. And also, its change to insoluble fibrin is essential for blood clotting.
The residual plasma proteins (1%) control the activity of proteins such as enzymes, proenzymes, and hormones. Blood proteins are typically manufactured in the liver.
Nutrients and Hormones
Blood plays a part in the purposes of the endocrine system. Nutrients, including glucose, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids. And also,There are absorbed from the bloodstream through tubes in intestinal villi. These nutrients are transported along with blood to many structures of the body. Blood also serves as a medium for hormones secreted by the endocrine system’s glands. A carrying them to their target tissues so they can exert their properties.
How Much Do You Have to Weigh to Donate Blood?
| Donor Category | Minimum Weight Requirement | Additional Notes |
| Standard Adult Donor | 110 lb (50 kg) | Most countries require this to ensure donor safety. |
| Teen Donors (16–17 years) | 110–130 lb (50–59 kg) | Some regions require higher weight and parental consent. |
| Plasma Donation | 110 lb (50 kg) | Donation pressure may vary based on weight. |
| Platelet Donation | 110 lb (50 kg) | Higher platelet count may be required. |
| Double Red Cell Donation | 130 lb (59 kg) | Higher weight needed due to increased red cell removal. |
| Underweight Individuals | Not | Low body weight increases risk of dizziness or fainting. |
Blood Deficiency in India, the UK, USA, London, and China
Here’ of blood deficiency in India, the UK, the USA, and China are limited:
| Region | Approx. Anemia | Source / Notes |
| India | 24–45% | Rates vary by age and sex; adolescents and women show high anemia prevalence e.g., 44% in girls, 41% adult women. |
| India | 39.9% | India had the highest anemia prevalence among 16 major countries, at 39.86%. |
| UK | 6.0% | UK data suggest a 6.0% prevalence of anemia in separated adults. |
| USA | 8.8–15.8% | In developed countries, the differences in US anemia was 8.8% and 15.8% in the general population, which is lower than in developing regions. |
| China | 8.9% | Age-standardized anemia prevalence in China was 8.9% in 2021. |
| London | 4.1% | England’s primary care data reported a 4.1% prevalence of anemia pre-COVID |
Overview: Blood is in The Human Body
Here is an overview table of how many pints of plasma are in the human body:
| Category | Average Blood pressure (Pints) | In Liters (Approx.) | Notes |
| Male | 9 – 10 | 4.5 – 5.5 L | Regularly higher due to greater body size |
| Female | 8 – 9 | 4.0 – 4.8 L | Somewhat lower on regular |
| Average Adult | 8 – 10 | 4.5 – 5.0 L | It is contingent on height and weight |
| Children | 4 – 6 | 2.0 – 3.0 L | Differs by age and development |
| Newborn Baby | 1 – 2 | 0.5 – 1.0 L | Very minor blood size |
Conclusion
Blood pressure varies based on age, weight, and sex. An adult male about 6 feet tall, weighing about 200 pounds. And also, It has about 12 pints of blood. The bone marrow produces the cellular workings. If red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
Medical interventions, such as blood transfusions, might be needed if bleeding reduces blood pressure significantly. In which can produce shock. Laboratory testing and physical inspection. It can control the extent of blood loss and the required interventions.
FAQS
- Does blood pressure vary by gender?
Yes, men naturally have slightly more blood than women. - How many liters of blood does the body have?
The human body contains about 4.5 to 5.5 liters of blood. - Is blood pressure associated with body weight?
Yes, blood brands up nearly 7–8% of body weight. - Is it harmless to lose some blood?
Yes, small quantities can be safely lost or donated under medical direction. - How much blood is taken throughout a donation?
About one pint of blood is taken in an average contribution. - Can the body substitute lost blood?
Yes, the body logically replaces lost blood over time.
Check this website: https://www.hlffitness.com/